Introduction
The plant-based market is often framed in extremes, either as a breakout success story or a category in decline. In reality, neither view reflects what’s happening on shelf today. Plant-based isn’t disappearing; it’s evolving.
Rather than focusing on a single year of performance, a longer-term view reveals how the category formed, scaled, and entered its current phase. This perspective offers clearer insight into where plant-based stands today, and why its next phase of growth will look different from the last.
A Decade of Change
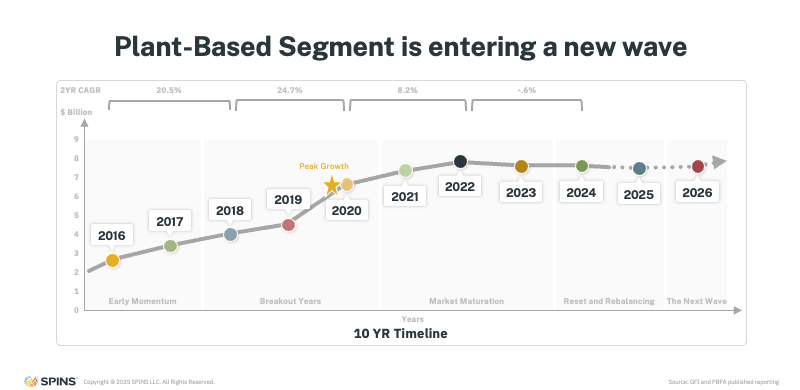
Modern plant-based began taking shape between 2016 and 2018, when traditional animal-based categories expanded into plant-based alternatives like milk and meat. Early innovation reframed plant-based as an aspirational choice tied to health, sustainability, and progress, driving rapid consumer trial.
Momentum accelerated through 2020, with growth peaking as shoppers experimented more and retailers expanded shelf space. Innovation surged, and assortments widened quickly.
Between 2020 and 2022, the category entered a maturation phase. Shelves became crowded, competition intensified, and not every product could sustain performance. This marked the beginning of a reset— where assortments tightened, weaker products exited, and retailers focused on what consumers consistently wanted.
Today’s flat to modest declines reflect recalibration, not collapse. Like many emerging categories before it, plant-based is moving from broad experimentation to a more disciplined, performance-driven phase.
Recent headlines suggesting plant-based is “dead” miss the larger context. Categories often follow a familiar arc: rapid growth, saturation, reassessment, and reinvention. Plant-based is firmly in that reinvention stage.
The next wave will be shaped by sharper innovation, clearer value propositions, and products that align with how consumers actually shop and eat today.
How Digital Discovery Is Reshaping Demand
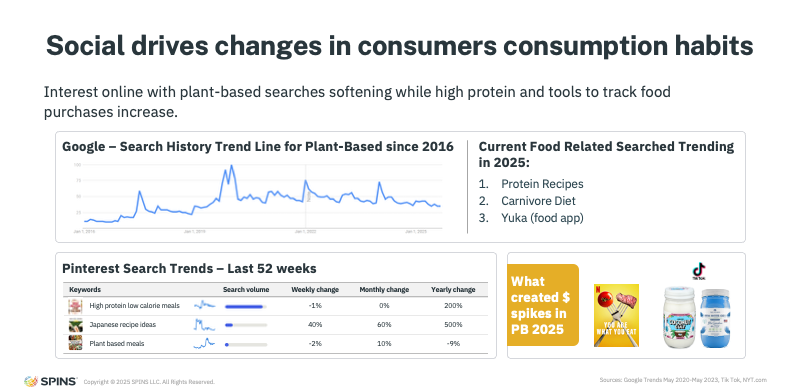
Shifts in consumer behavior are also influencing plant-based performance. Social media and online search now play a central role in how shoppers discover and evaluate products, often before they ever reach the shelf.
Gen Z consumers increasingly rely on platforms like TikTok and Instagram for product discovery, while Millennials turn to more traditional channels like Google, Facebook & Youtube. This digital-first path to discovery is reshaping which products gain traction in-store.
Search trends reinforce this shift. Rather than showing a sharp rise and fall, interest in plant-based fluctuates throughout the year, alongside broader searches for high-protein diets, low-carb eating, and product-rating apps like Yuka. Cultural moments, such as documentaries or viral social trends, continue to drive temporary but meaningful spikes in interest and trial.
Retail Drivers and Decliners: Where Plant-Based Is Stabilizing, and Why
As plant-based enters its next phase, retail performance data shows early signs of stabilization. While the category is still working through a reset, underlying trends suggest improving momentum and clearer signals about where growth is concentrating, and where it is not.
Plant-Based Declines Begin to Lessen Heading Toward 2026
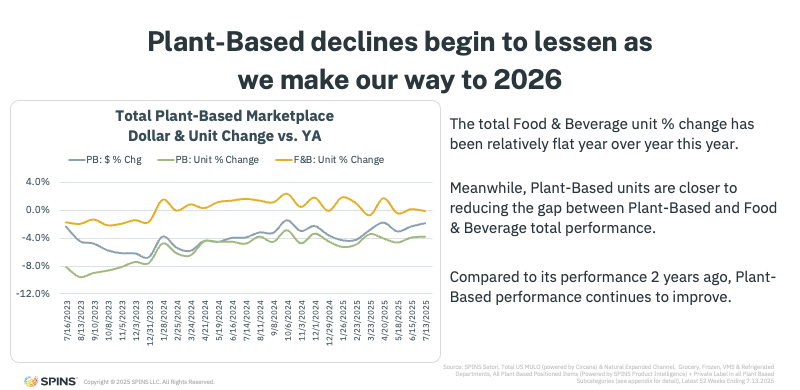
Looking across the total store, plant-based trends are no longer deteriorating at the pace seen earlier in the reset period. When evaluating two-year trends from 2023 through 2025, declines in plant-based units have narrowed significantly.
Compared to total food and beverage performance, plant-based once showed a wide gap, reaching declines as steep as 8–10% in 2023. By 2025, that gap has narrowed considerably to 4%. In other words, losses have been reduced by roughly half.
This improvement matters. It reinforces that the category is not continuing to slide unchecked, but instead finding a more stable footing. As the reset progresses, performance is becoming less volatile, an encouraging signal for both brands and retailers navigating assortment decisions.
The takeaway: plant-based is still in recalibration mode, but the direction of travel is improving.
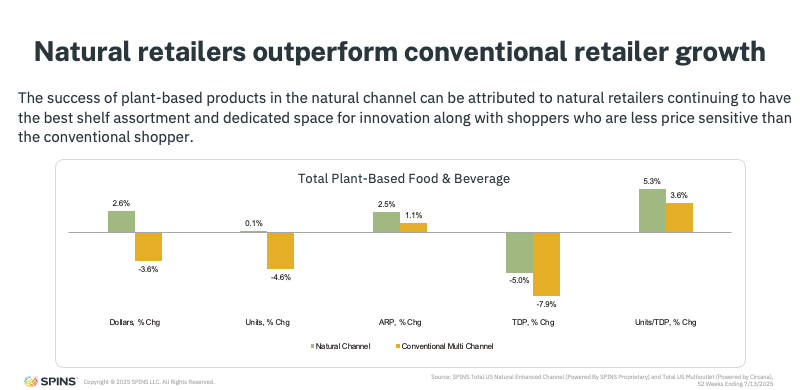
Natural Retailers Continue to Outperform Conventional Channels
One of the clearest explanations for improving trends lies in channel performance. When natural and conventional retailers are viewed separately, the divergence is unmistakable.
Natural retailers are growing, up more than 2%, while conventional retailers are seeing continued declines of more than 3%. Growth in the natural channel is being driven by several structural advantages:
- Stronger shelf assortments, with more relevant and differentiated plant-based options
- Earlier adoption of innovation, which often launches first in natural retail
- Lower price sensitivity, allowing shoppers to absorb premium positioning more easily
At the same time, broader economic pressures are shaping behavior across both channels. Inflation, tariffs, and price increases are impacting average retail prices, with sharper increases visible in natural retail. Distribution has also declined, reflecting tighter inventory management as retailers reduce risk and carrying costs.
Assortments are smaller. Fewer new items are being accepted. But despite these constraints, one metric stands out: velocity is up.
Units per point of distribution are increasing across channels, indicating that products still on shelf are moving faster. Demand has not disappeared. Shoppers are still buying plant-based, just more selectively.
This suggests that the category’s challenge is no longer consumer interest, but precision: having the right products on shelf.
What’s Driving Growth, and What’s Falling Behind
As assortments tighten, growth is concentrating in specific product types and attributes that align with broader shopper priorities.
Plant-based growth is increasingly tied to protein-forward and functional benefits, particularly:
- Gut health–oriented products, a trend that continues to build across food and beverage
- Protein-enhanced items, including smoothies, shakes, yogurt-based snacks, bars, tofu, and meal replacements
- Refrigerated beverages, where drinkable nutrition and convenience intersect
These categories reflect a consistent throughline: shoppers are seeking plant-based products that deliver tangible nutritional benefits, especially protein, without sacrificing convenience.
There is also room for intentional indulgence. While many shoppers are watching carbs and increasing protein intake, indulgent plant-based items in categories like cookie and pastry doughs continue to find an audience. The data reinforces that health-driven eating does not eliminate desire for treat moments, it simply reframes them.
On the flip side, products that lack clear functional benefits or fail to differentiate on nutrition, taste, or usage occasion are struggling to maintain shelf presence. As retailers prioritize velocity and efficiency, products that once benefited from novelty alone are being phased out.
Competition Is Raising the Bar
As plant-based enters its next phase, performance shifts can’t be understood by looking at plant-based in isolation. What’s happening now is the result of intensified competition, both within plant-based and from animal-based categories that are evolving just as quickly to meet changing consumer expectations.
To understand these dynamics, it’s necessary to look deeper at consumer behavior: who is buying, who is leaving, and where those dollars are going.
Recent changes in plant-based performance reflect broader shifts in how consumers evaluate food choices. As shoppers become more informed and more intentional, they are reassessing what value means to them, whether that’s nutrition, ingredient quality, price, or perceived health benefits.
By analyzing consumer-level purchase behavior rather than just top-line sales, a clearer picture emerges. These shifts are not random. They are rooted in evolving expectations and a growing set of alternatives competing for the same occasions.
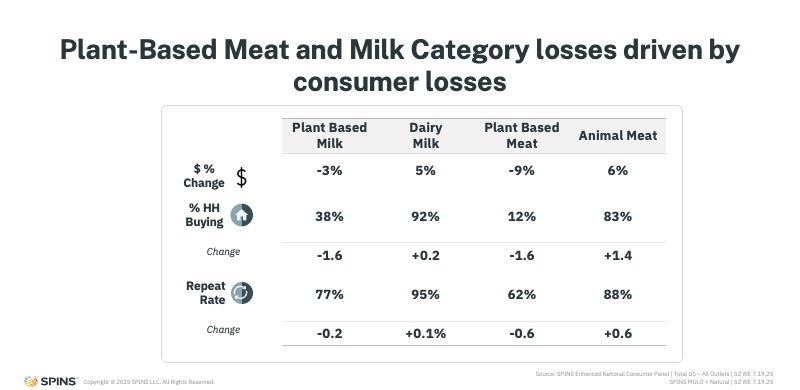
Plant-Based Meat and Milk Losses Are Driven by Consumer Attrition
Plant-based meat and plant-based milk are both experiencing declines in dollar sales, but those losses don’t exist in a vacuum.
At the same time plant-based meat and milk are softening, traditional animal-based meat and dairy milk are seeing slight dollar growth. This growth is being supported by modest increases in household penetration over the past year.
Repeat behavior tells a similar story. Animal meat and dairy milk are seeing slight increases in repeat rates, while plant-based meat and milk are experiencing small declines. This divergence suggests that some consumers are reassessing their choices, reducing or replacing plant-based purchases rather than abandoning categories altogether.
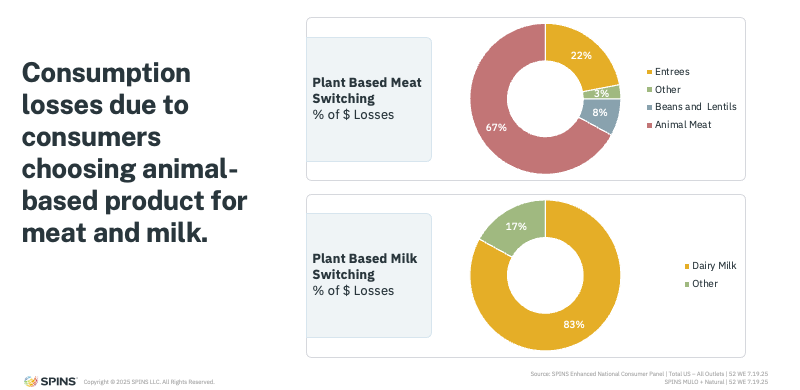
Consumption Losses Reflect Switching Back to Animal-Based Options
To understand where plant-based dollars are going, switching behavior provides critical insight.
For plant-based meat, the majority of dollar losses, roughly two-thirds, are shifting back to animal meat. However, the picture is more nuanced than a simple reversal. Some volume is also moving into adjacent categories like prepared refrigerated entrées, as well as beans and lentils, indicating that both flexitarian shoppers and plant-forward consumers may be adjusting how they source protein.
Plant-based milk shows a more concentrated shift. More than four-fifths of the dollar losses in this category are moving back to dairy milk. This suggests that for many shoppers, dairy is regaining relevance, especially as product quality and perceived health benefits improve.
The key takeaway: consumers aren’t leaving food categories, they’re reallocating spending toward products that better match their current priorities.
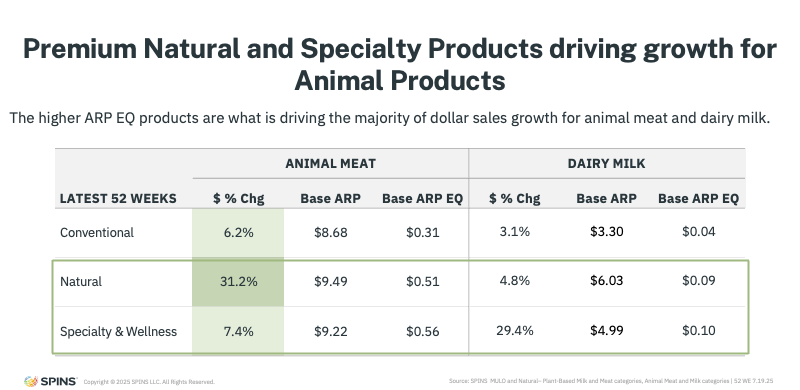
Premium Natural and Specialty Animal Products Are Gaining Share
The growth in animal-based categories isn’t coming from traditional commodity products alone. Instead, it’s being driven by premium natural and specialty offerings.
Across both meat and dairy, products positioned around wellness, quality, and transparency are gaining dollars and units. These products often emphasize cleaner ingredients, higher standards of sourcing, and improved nutritional profiles, aligning closely with what plant-based once uniquely offered.
When examining which brands are outperforming, a clear pattern emerges: growth is concentrated among “better-for-you” animal-based options that mirror the values consumers associate with health-forward eating.
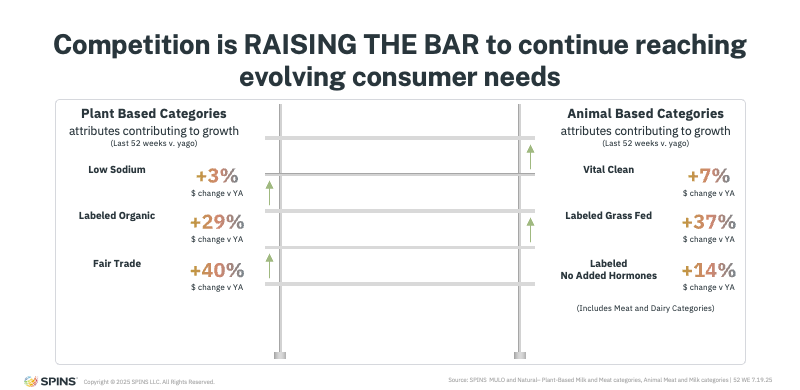
Competition Is Raising the Bar Across the Store
This moment reflects a broader competitive reality. The early growth of plant-based between 2015 and 2020 was fueled by strong consumer belief that plant-based products were inherently healthier and more progressive. But during that same period, animal-based categories didn’t stand still.
Innovation accelerated across meat and dairy. Products were reformulated, ingredients were cleaned up, and new claims became mainstream, such as grass-fed, hormone-free, antibiotic-free, and clean-label positioning. These attributes are now key drivers of dollar growth in animal-based categories.
As a result, competition between plant-based and animal-based products has intensified. While the categories are fundamentally different, they increasingly compete for the same consumers, the same meal occasions, and the same health-driven motivations.
What’s happening now is not a rejection of plant-based, but a recalibration of expectations. Consumers are comparing options more critically, and whichever product best delivers on taste, nutrition, transparency, and value is earning the purchase.
What’s Working in Plant-Based to Drive Consumption
Despite the broader reset, plant-based continues to perform when it delivers clear value to shoppers. By examining the attributes behind products that are still growing, a consistent pattern emerges: success is less about being plant-based in name and more about what the product delivers nutritionally, functionally, and ethically.
The strongest performers are not trying to compete on ideology alone. They are competing on benefits consumers actively seek across the total store.
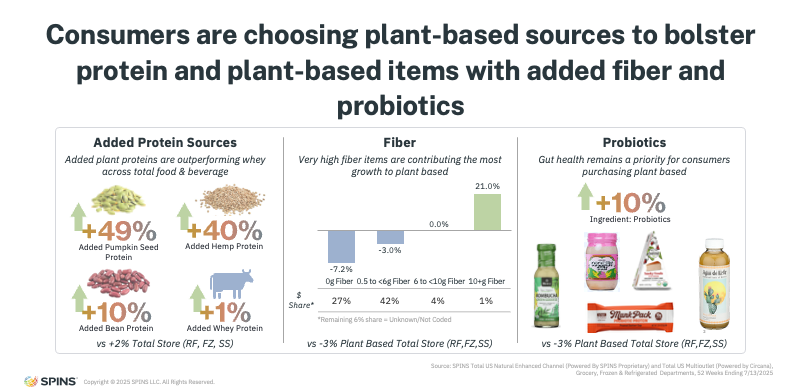
Added Nutritional Value Is a Core Growth Driver
One of the most resilient drivers of plant-based consumption is added nutritional value, particularly protein and fiber.
Plant-based protein remains highly relevant across food and beverage, even as some shoppers reconsider plant-based meat and dairy alternatives. Consumers may be changing where they source protein, but enthusiasm for plant-based protein itself remains strong, especially when it is added to familiar, convenient formats.
Fiber is another standout. High-fiber plant-based products are outperforming not only the rest of plant-based, but the total store as well. This strength is being fueled by heightened consumer interest in digestive health, metabolic wellness, and dietary balance, trends further amplified by the rise of GLP-1 medications and broader conversations around satiety and gut health. Fiber-forward plant-based products are not a short-term trend; they are becoming a baseline expectation.
Probiotics represent another major growth pocket. Plant-based products containing probiotics are significantly outperforming the category overall, reflecting a preference, particularly among younger consumers, to get digestive support from foods rather than supplements. Yogurt-based products exemplify this trend, combining convenience, protein, and probiotic benefits in a format that fits modern eating habits. As digestive health remains top of mind, probiotic-rich plant-based foods are well positioned for continued growth.
Functionality Is Fueling the Next Phase of Innovation
Functional ingredients are playing an increasingly important role in plant-based performance. Products featuring ingredients such as matcha, functional mushrooms, and maca root are outperforming the category, driven by their association with energy, mood, focus, and overall wellness.
These ingredients have broad appeal because they offer benefits that resonate across lifestyles, not just within plant-based diets. Matcha’s popularity has surged to the point of supply constraints, while functional mushrooms continue to defy expectations of saturation, maintaining strong momentum year after year.
This sustained performance reflects a shift in how consumers think about food: not just as fuel, but as a tool to support daily performance and emotional well-being. Plant-based products that deliver on these functional promises are earning repeat engagement, particularly with Gen Z and Millennials.
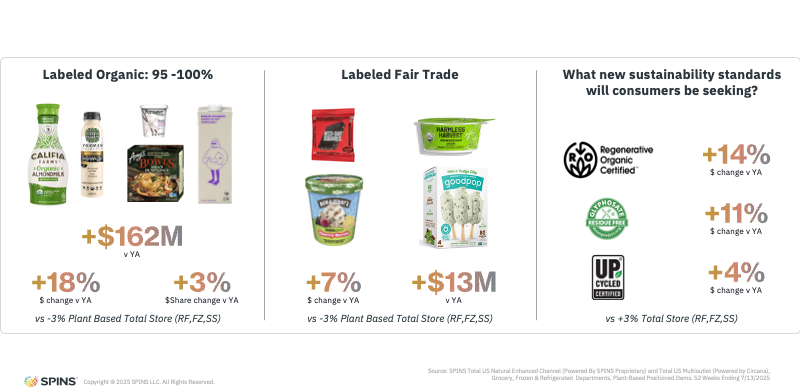
Sustainability Attributes Are Reaccelerating Growth
Sustainability remains deeply intertwined with plant-based consumption, and is becoming an even stronger differentiator as availability improves.
Organic plant-based products are seeing particularly strong growth, far outpacing both the category and the total store. This reflects pent-up demand: shoppers who prioritize plant-based eating also tend to value organic sourcing, and recent expansion of organic plant-based options is meeting that need in a meaningful way.
Other sustainability attributes are also gaining traction. Fair trade certifications continue to resonate with consumers seeking ethical sourcing and social responsibility. Regenerative organic products are beginning to make a noticeable impact as ingredient supply expands and more brands bring these claims to market. As awareness grows, regenerative practices are likely to play a larger role in plant-based differentiation.
Glyphosate residue–free claims are emerging as another point of trust, particularly for plant-based products made with grains, oats, beans, and flax, ingredients where contamination concerns are more top of mind. These certifications provide reassurance for consumers who want greater transparency and confidence in what they’re consuming.
Upcycled ingredients round out this set of sustainability drivers. While adoption took time, upcycled plant-based products are gaining momentum as consumers embrace solutions that reduce food waste while still delivering quality and taste.
Entering the Next Evolution Stage of Plant-Based
Looking ahead to 2026 and beyond, plant-based is increasingly defined by the priorities of the conscious consumer, shoppers who scrutinize ingredients, sourcing, and production practices as closely as taste and nutrition.
One of the clearest examples is growing awareness around glyphosate and its role in conventional farming systems. For many early adopters and health-focused consumers, concerns around chemical exposure, soil health, and sustainable agriculture are influencing purchasing decisions across plant-based dairy alternatives, yogurts, frozen novelties, and creamers.
These conversations are no longer niche. They’re happening at the farm level, within brand strategy, at retail, and around the dinner table. As transparency expectations rise, plant-based products that proactively address these concerns are better positioned to earn trust and loyalty in the years ahead.
Innovation Is Concentrating Around Trending Nutrients
Not all plant-based categories are innovating at the same pace, and that difference matters.
Categories tied to trending nutrients, particularly protein, are seeing higher innovation rates and stronger growth. Wellness bars, snack bars, protein powders, ready-to-drink shakes, smoothies, and juices are all attracting significant new product development. In these formats, consumers are less concerned with where protein comes from and more focused on how much they’re getting and how easily it fits into their routine.
Plant-based yogurt stands out as a particularly strong performer. Products made with coconut and other plant bases are gaining traction not just among plant-based shoppers, but also among flexitarian and traditional dairy consumers. Added probiotic benefits and strong nutritional profiles make these products an easy switch for shoppers seeking digestive support without sacrificing taste or convenience.
In short, innovation is working best where plant-based aligns with existing consumption habits, rather than trying to replace them entirely.
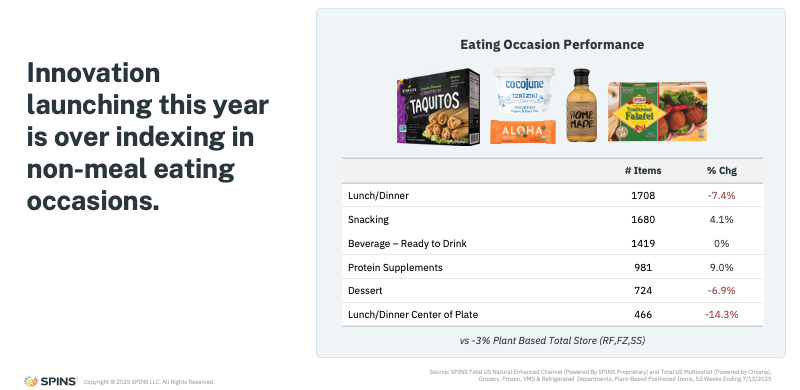
Innovation Is Shifting Toward Non-Meal Occasions
Another defining characteristic of the next wave is where plant-based shows up in the day.
Innovation tied to lunch and dinner occasions, especially center-of-plate replacements, is slowing. Instead, new plant-based products are increasingly launching for non-meal occasions:
- Snacking
- Beverages
- Protein supplements
- Desserts
These are areas where plant-based feels additive rather than substitutive, complementing how consumers already eat rather than asking them to overhaul familiar habits.
At the same time, international flavors are playing a growing role. Many global cuisines, particularly Asian and Middle Eastern, are inherently more plant-forward, relying less on meat and dairy.
As these flavors continue to gain popularity in both retail and foodservice, they create natural entry points for plant-based products that feel authentic rather than forced.
This shift reflects a broader redefinition of the “modern kitchen,” where eating occasions are more flexible, global, and individualized.
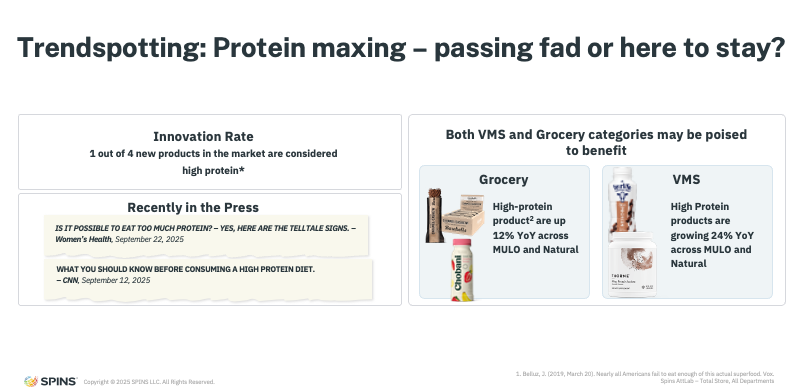
Trendspotting: Protein Maxing, Passing Fad or Staying Power?
Protein remains one of the most influential forces shaping innovation, but signs suggest the market may be approaching a more mature phase.
High-protein products continue to grow strongly across grocery, mass, and club channels, with roughly one in four new product launches now carrying a high-protein claim. Continued growth in protein supplements indicates that consumer interest remains high.
That said, early signals of moderation are emerging. Growth has begun to slow in natural retail, and media narratives are starting to question whether extreme protein intake is always beneficial. Another cautionary sign: the growing number of highly processed foods repositioned as “healthy” simply by adding protein, often a turning point seen in previous cycles around fat and sugar.
The takeaway isn’t that protein is going away, but that scrutiny is increasing. The next phase of protein innovation will likely favor quality, balance, and credibility over sheer quantity.
Consumer Values Continue to Align With What Plant-Based Delivers
At its core, plant-based continues to align with the values that matter most to modern consumers.
Year after year, shoppers prioritize products that are good for personal health, animals, people, and the planet. Plant-based diets consistently intersect with these priorities, offering benefits tied to reduced disease risk, lower environmental impact, and more efficient food systems.
From a sustainability perspective, plant-based agriculture has the potential to significantly reduce carbon footprints and resource use. From a human standpoint, a broader shift toward plant-forward diets could improve global food security and support a growing population.
These values are not cyclical trends, they are long-term drivers of consumer behavior. And they provide a durable foundation for plant-based as the category continues to evolve.
The Next Chapter of Plant-Based Growth
Plant-based is no longer a category defined by experimentation or extremes, it is entering a more deliberate, data-informed phase of growth. As consumer expectations rise, success will hinge on clarity: clear benefits, clear differentiation, and clear alignment with how people actually shop, eat, and make decisions today.
The next wave of plant-based will be led by products that earn trust, deliver real value, and evolve alongside broader shifts in health, sustainability, and culture. For brands and retailers willing to adapt, this moment is not a turning point away from plant-based, but an opportunity to shape what it becomes next.
Taken together, the data and insights throughout this analysis point to a clear set of conclusions that define where the category stands today and what will matter most moving forward:
- Plant-Based segment is in a place of reset and not a collapse.
- Consumer trends and more natural animal-based products swung a group of consumers back to animal products.
- Consumption of plant-based products continue to grow in non-staple categories with cleaner, better-for-you options that win on taste.
- The next wave of plant-based depends on brands bringing more innovation that drives consumers to switch.